About Medicine
Human G-CSF is a glycoprotein which regulates the production and release of functional neutrophils from the bone marrow. PDgrastim® containing r-metHuG-CSF (filgrastim) causes marked increases in peripheral blood neutrophil counts within twenty-four hours, with minor increases in monocytes. Use of filgrastim in patients undergoing cytotoxic chemotherapy leads to significant reductions in the incidence, severity and duration of neutropenia and febrile neutropenia. Treatment with filgrastim significantly reduces the durations of febrile neutropenia, antibiotic use and hospitalization after induction chemotherapy for acute myelogenous leukemia or myeloablative therapy followed by bone marrow transplantation.
Pharmaceutical form
Prefilled syringes: 300 μg Filgrastim (equivalent 30 MIU Filgrastim) in 0.5 mL
Qualitative composition
Sterile solution, clear and colorless in prefilled syringe
Guidance to patients
Overdosage
If you think that you have used too much or too little PDgrastim®, tell your doctor, nurse or pharmacist immediately, even if you have no signs of a problem.
What if you forget to use PDgrastim®?
If you forget to give yourself a dose, have it as soon as you remember. Do not give yourself a double dose on the same day to make up for a forgotten dose. Keeping a diary will help to make sure you do not miss a dose.
Effect on Ability to Drive and Operate Machinery
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
Use
- PDgrastim® is indicated for the reduction in the duration of neutropenia and the incidence of febrile neutropenia in patients treated with established cytotoxic chemotherapy for malignancy (with the exception of chronic myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes) and for the reduction in the duration of neutropenia in patients undergoing myeloablative therapy followed by bone marrow transplantation considered to be at increased risk of prolonged severe neutropenia. The safety and efficacy of PDgrastim® are similar in adults and children receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy.
- PDgrastim® is indicated for the mobilization of peripheral blood progenitor cells (PBPCs).
- In patients, children or adults, with severe congenital, cyclic, or idiopathic neutropenia with an ANC of ≤ 0.5 x 109/l, and a history of severe or recurrent infections, long term administration of PDgrastim® is indicated to increase neutrophil counts and to reduce the incidence and duration of infection-related events.
- PDgrastim® is indicated for the treatment of persistent neutropenia (ANC less than or equal to 1.0 x 109/l) in patients with advanced HIV infection, in order to reduce the risk of bacterial infections when other options to manage neutropenia are inappropriate.
- Patients Acutely Exposed to Myelosuppressive Doses of Radiation (Hematopoietic Syndrome of Acute Radiation Syndrome): PDgrastim is indicated to increase survival in patients acutely exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation.
Dosing: Adult
PDgrastim® therapy should only be given in collaboration with an oncology center which has experience in G-CSF treatment and hematology and has the necessary diagnostic facilities.
1. Established cytotoxic chemotherapy
The recommended dose of PDgrastim® is 5 µg/kg/day. The first dose of PDgrastim® should be administered at least 24 hours after cytotoxic chemotherapy.
Daily dosing with PDgrastim® should continue until the expected neutrophil nadir is passed and the neutrophil count has recovered to the normal range. Following established chemotherapy for solid tumors, lymphomas, and lymphoid leukemia, it is expected that the duration of treatment required to fulfil these criteria will be up to 14 days. Following induction and consolidation treatment for acute myeloid leukemia the duration of treatment may be substantially longer (up to 38 days) depending on the type, dose and schedule of cytotoxic chemotherapy used.
In patients receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy, a transient increase in neutrophil counts is typically seen 1 to 2 days after initiation of PDgrastim® therapy. However, for a sustained therapeutic response, PDgrastim® therapy should not be discontinued before the expected nadir has passed and the neutrophil count has recovered to the normal range. Premature discontinuation of PDgrastim® therapy, prior to the time of the expected neutrophil nadir, is not recommended.
Method of administration
PDgrastim® may be given as a daily subcutaneous injection or as a daily intravenous infusion diluted in 5% glucose solution given over 30 minutes. The subcutaneous route is preferred in most cases. There is some evidence from a study of single dose administration that intravenous dosing may shorten the duration of effect. The clinical relevance of this finding to multiple dose administration is not clear. The choice of route should depend on the individual clinical circumstance.
2. In patients treated with myeloablative therapy followed by bone marrow transplantation
The recommended starting dose of PDgrastim® is 10 µg/kg/day. The first dose of PDgrastim® should be administered at least 24 hours following cytotoxic chemotherapy and at least 24 hours after bone marrow infusion.
Once the neutrophil nadir has been passed, the daily dose of PDgrastim® should be titrated against the neutrophil response as follows:
Neutrophil Count
PDgrastim® Dose Adjustment > 1.0 x 109/l for 3 consecutive days
Reduce to 5 µg/kg/day
Then, if ANC remains > 1.0 x 109/l for 3 more consecutive days
Discontinue PDgrastim®
If the ANC decreases to < 1.0 x 109/l during the treatment period the dose of PDgrastim® should be re-escalated according to the above steps ANC = absolute neutrophil count
Method of administration
PDgrastim® may be given as a 30 minute or 24 hour intravenous infusion. PDgrastim® should be diluted in 20 ml of 5% glucose solution.
3. In patients with severe chronic neutropenia (SCN)
Congenital neutropenia
The recommended starting dose is 12 µg/kg/day, as a single dose or in divided doses.
Idiopathic or cyclic neutropenia
The recommended starting dose is 5 µg/kg/day as a single dose or in divided doses.
Dose adjustment
PDgrastim® should be administered daily by subcutaneous injection until the neutrophil count has reached and can be maintained at more than 1.5 x 109/l. When the response has been obtained the minimal effective dose to maintain this level should be established. Long term daily administration is required to maintain an adequate neutrophil count. After one to two weeks of therapy, the initial dose may be doubled or halved depending upon the patient’s response. Subsequently the dose may be individually adjusted every 1 to 2 weeks to maintain the average neutrophil count between 1.5 x 109/l and 10 x 109/l. A faster schedule of dose escalation may be considered in patients presenting with severe infections. In clinical trials, 97% of patients who responded had a complete response at doses ≤ 24 µg/kg/day. The long-term safety of PDgrastim® administration above 24 µg/kg/day in patients with SCN has not been established.
Method of administration
Congenital, idiopathic or cyclic neutropenia: PDgrastim® should be given by subcutaneous injection.
4. For the mobilization of PBPCs in patients undergoing myelosuppressive or myeloablative therapy followed by autologous PBPC transplantation
The recommended dose of PDgrastim® for PBPC mobilization when used alone is 10 µg/kg/day for 5 to 7 consecutive days. Timing of leukapheresis: one or two leukapheresis on days 5 and 6 are often sufficient. In other circumstances, additional leukapheresis may be necessary. PDgrastim® dosing should be maintained until the last leukapheresis.
The recommended dose of PDgrastim® for PBPC mobilization after myelosuppressive chemotherapy is 5 µg/kg/day from the first day after completion of chemotherapy until the expected neutrophil nadir is passed and the neutrophil count has recovered to the normal range. Leukapheresis should be performed during the period when the ANC rises from < 0.5 x 109/l to > 5.0 x 109/l. For patients who have not had extensive chemotherapy, one leukapheresis is often sufficient. In other circumstances, additional leukapheresis are recommended.
Method of administration
PDgrastim® should be given by subcutaneous injection.
5. For the mobilization of PBPCs in normal donors prior to allogeneic PBPC transplantation
For PBPC mobilization in normal donors, PDgrastim® should be administered at 10 µg/kg/day for 4 to 5 consecutive days. Leukapheresis should be started at day 5 and continued until day 6 if needed in order to collect 4 x 106 CD34+cells/kg recipient bodyweight.
Method of administration
PDgrastim® should be given by subcutaneous injection.
6. In patients with HIV infection
For reversal of neutropenia:
The recommended starting dose of PDgrastim® is 1 µg/kg/day, with titration up to a maximum of 4 µg/kg/day until a normal neutrophil count is reached and can be maintained (ANC > 2.0 x 109/l). In clinical studies, > 90% of patients responded at these doses, achieving reversal of neutropenia in a median of 2 days. In a small number of patients (< 10%), doses up to 10 µg/kg/day were required to achieve reversal of neutropenia.
For maintaining normal neutrophil counts:
When reversal of neutropenia has been achieved, the minimal effective dose to maintain a normal neutrophil count should be established. Initial dose adjustment to alternate day dosing with 300 µg/day is recommended. Further dose adjustment may be necessary, as determined by the patient’s ANC, to maintain the neutrophil count at > 2.0 x 109/l. In clinical studies, dosing with 30 MU (300 µg)/day on 1 to 7 days per week was required to maintain the ANC > 2.0 x 109/l, with the median dose frequency being 3 days per week. Long term administration may be required to maintain the ANC > 2.0 x 109/l.
7. Dosage in Patients Acutely Exposed to Myelosuppressive Doses of Radiation (Hematopoietic Syndrome of Acute Radiation Syndrome):
The recommended dose of PDgrastim is 10 mcg/kg as a single daily subcutaneous injection for patients exposed to myelosuppressive doses of radiation. Administer PDgrastim as soon as possible after suspected or confirmed exposure to radiation doses greater than 2 gray (Gy). Estimate a patient’s absorbed radiation dose (i.e., level of radiation exposure) based on information from public health authorities, biodosimetry if available, or clinical findings such as time to onset of vomiting or lymphocyte depletion kinetics. Obtain a baseline CBC and then serial CBCs approximately every third day until the ANC remains greater than 1,000/mm 3 for 3 consecutive CBCs. Do not delay administration of PDgrastim if a CBC is not readily available. Continue administration of PDgrastim until the ANC remains greater than 1,000/mm 3 for 3 consecutive CBCs or exceeds 10,000/mm 3 after a radiation-induced nadir.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to Filgrastim, Pegfilgrastim, coli -derived proteins, or any component of the formulation
- Kostmann’s syndrome
- PDgrastim® should not be used to increase the dose of cytotoxic chemotherapy beyond established dosage regimens.
- PDgrastim® should not be administered to patients with severe congenital neutropenia who develop leukemia or have evidence of leukemic evolution.
Warnings and precautions
- Hypersensitivity, including anaphylactic reactions, occurring on initial or subsequent treatment has been reported in patients treated with PDgrastim®. Permanently discontinue PDgrastim® in patients with clinically significant hypersensitivity. Do not administer PDgrastim® to patients with a history of hypersensitivity to filgrastim or pegfilgrastim.
- PDgrastim® should not be diluted with saline solutions. If required, PDgrastim® may be diluted in 5% glucose. Dilution to a final concentration less than 2 µg/ml is not recommended at any time.
- Concurrent drug therapy issues:
- Cytotoxic chemotherapy: Do not use filgrastim in the period 24 hours before to 24 hours after administration of cytotoxic chemotherapy because of the potential sensitivity of rapidly dividing myeloid cells to cytotoxic chemotherapy.
- The safety and efficacy of PDgrastim® administration in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome, or chronic myelogenous leukemia have not been established.
- Monitoring of bone density may be indicated in patients with underlying osteoporotic bone diseases who undergo continuous therapy with PDgrastim® for more than 6 months.
- Pulmonary adverse effects, in particular interstitial lung disease, have been reported after G-CSF administration. Patients with a recent history of lung infiltrates or pneumonia may be at higher risk. The onset of pulmonary signs, such as cough, fever and dyspnea in association with radiological signs of pulmonary infiltrates and deterioration in pulmonary function may be preliminary signs of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). PDgrastim® should be discontinued and appropriate treatment given.
- Capillary leak syndrome has been reported after granulocyte colony-stimulating factor administration, and is characterized by hypotension, hypoalbuminemia, edema and hemoconcentration. Patients who develop symptoms of capillary leak syndrome should be closely monitored and receive standard symptomatic treatment, which may include a need for intensive care.
- Splenic rupture: Rare cases of splenic rupture have been reported (may be fatal); patients must be instructed to report left upper quadrant pain or shoulder tip pain.
- Disease-related concerns:
- Sickle cell disorders: May precipitate severe sickle cell crises, sometimes resulting in fatalities, in patients with sickle cell disorders; carefully evaluate potential risks and benefits.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Risk Factor is C. Animal studies have demonstrated adverse effects and fetal loss. Filgrastim has been shown to cross the placenta in humans. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Use only if potential benefit to mother justifies risk to the fetus.
Lactation
Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) is a normal component of breastmilk. However, the excretion of exogenous filgrastim in breastmilk or its effects on breastfed infants have not been well studied. Limited data indicate that filgrastim and a similar G-CSF product, lenograstim, are poorly excreted into breastmilk and are undetectable by 3 days after an injection. Some authors recommend withholding breastfeeding for this period of time. However, filgrastim has been safely given orally to neonates and is not orally absorbed by neonates, so any filgrastim that is excreted into milk is unlikely to adversely affect the breastfed infant.
Adverse effects
Very common (>10%)
- Blood uric acid increased
- Blood lactate dehydrogenase increased
- Decreased appetite
- Headache
- Oropharyngeal pain
- Cough
- Dyspnea
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Constipation
- Nausea
- Blood alkaline phosphatase increased
- Rash
- Alopecia
- Musculoskeletal pain
- Thrombocytopenia
- Leukocytosis
- Fatigue
- Mucosal inflammation
Common (1-10%)
- Drug hypersensitivity
- Hypotension
- Hemoptysis
- Dysuria
- Chest pain
- Injection site reaction
- Hematuria
Uncommon (0.1-1%)
- Splenic rupture
- Splenomegaly
- Sickle cell crisis
- Pseudo gout
- Fluid volume disturbances
- Capillary leak syndrome
- Acute respiratory distress syndrome
- Respiratory failure
- Pulmonary edema
- Interstitial lung disease
- Lung infiltration
- Pulmonary hemorrhage
- Sweets syndrome
- Cutaneous vasculitis
- Urine abnormality
- Pain
- Anaphylactic reaction
- Hyperuricaemia
Drug interactions
Bleomycin
Filgrastim may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Bleomycin. Specifically, the risk for pulmonary toxicity may be increased.
Topotecan
Filgrastim may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Topotecan.
Lithium
Combining these medications may increase the effects of filgrastim, which could lead to excessive numbers of certain types of blood cells.
Monitoring Parameters
CBC with differential and platelets prior to treatment and twice weekly during filgrastim treatment for chemotherapy-induced neutropenia (3times/week following marrow transplantation). For severe chronic neutropenia, monitor CBC with differential and platelets twice weekly during the first month of therapy and for 2 weeks following dose adjustments; once clinically stable, monthly for 1 year and quarterly thereafter; for congenital neutropenia also monitor bone marrow and karyotype prior to treatment; and monitor marrow and cytogenetics annually throughout treatment. Monitor temperature.
Mechanism of action
Human G-CSF is a glycoprotein which regulates the production and release of functional neutrophils from the bone marrow. PDgrastim® containing r-metHuG-CSF (filgrastim) causes marked increases in peripheral blood neutrophil counts within twenty-four hours, with minor increases in monocytes.
Pharmacokinetics
Onset of action: ~24 hours; plateaus in 3-5 days
Duration: Neutrophil counts generally return to baseline within 4 days
Absorption: SubQ: 100%
Distribution: Vd: 150 mL/kg
Metabolism: Systemically degraded
Half-life elimination: 8-3.5 hours
Time to peak, serum: SubQ: 2-8 hours
Guidance for injection
- Before use, leave the PDgrastim® syringe to stand until it reaches room temperature. This usually takes between 15 and 30 minutes. Do not remove the syringe’s needle cover while allowing it to reach room temperature.
- Only take one dose of PDgrastim® from each syringe.
- PDgrastim® is given alone and not mixed with other liquids for injection.
- Do not shake PDgrastim® Prolonged vigorous shaking may damage the product. If the product has been shaken vigorously, don’t use it.
- Check the syringe, to make sure it is the right dose, has not passed its expiry date, is not damaged, and the liquid is clear and not frozen.
- Choose an injection site. Do not inject PDgrastim® into an area that is tender, red, bruised, hard, or has scars or stretch marks. Recommended sites for injection are:
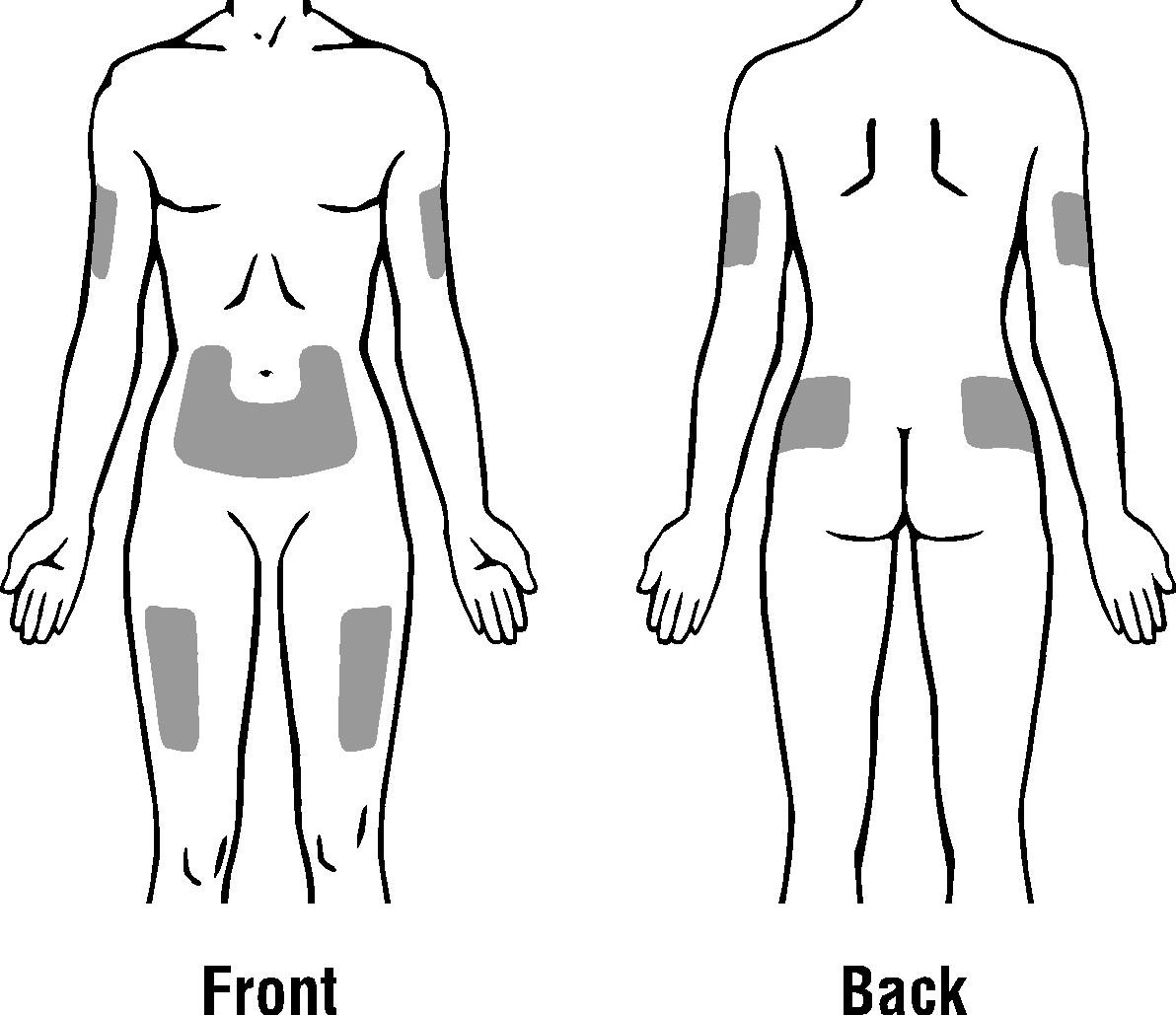
- The outer area of the upper arms
- The abdomen (except for the 2-inch area around the navel)
- The front of the middle thighs
- The upper outer area of the buttocks
- Wash your hands. Use an antiseptic swab on the injection site, to disinfect it.
- Hold the pre-filled syringe by the body of the syringe with the covered needle pointing upward.
- Do not hold by the plunger head, plunger or needle cover.
- Do not pull back on the plunger at any time.
- Do not remove the needle cover from the pre-filled syringe until you are ready to inject your PDgrastim®.
- Take the cover off the syringe by holding the barrel and pulling the cover off carefully without twisting it. Don’t push the plunger, touch the needle or shake the syringe.
- Pinch a fold of skin between your thumb and index finger. Don’t squeeze it.
- Push the needle in fully. Your doctor or nurse may have shown you how to do this.
- Push the plunger with your thumb as far as it will go to inject the entire amount of liquid. Push it slowly and evenly, keeping the skin fold pinched.
- When the plunger is pushed as far as it will go, take out the needle and let go of the skin.
- When the needle is pulled out of your skin, there may be a little bleeding at the injection site. This is normal. You can press an antiseptic swab over the injection site for a few seconds after the injection.
- Dispose of your used syringe in a safe container.
Storage and stability
- Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
- Keep the container in the outer carton in order to protect from light.
- Keep out of the reach and sight of children.
- Do not use PDgrastim® after the expiry date which is stated on the box and on the syringe label (EXP). The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
- Do not freeze PDgrastim® and do not use PDgrastim® that has been frozen or improperly refrigerated.
- Do not shake PDgrastim®.
- PDgrastim® pre-filled syringes are single dose containers, discard any unused product.
Other composition
Acetate sodium, Sorbitol, Polysorbate 80, Water for injection

